Looking back at the history of Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV), the evolution of navigation technology has been undoubtedly the most vivid footnote for the development of the industry.
In the early times, AGV needed track navigation, such as steel track navigation, electromagnetic navigation, magnetic nail navigation, etc., and the deployment and construction cost of navigation facilities were high. Since the 21st century, 2D LiDAR backed natural navigation technologies gained momentum in the AGV field, and navigation technologies such as QR code were introduced at the same time, further reducing unmanned forklifts’ dependence on site facilities and cost of facility deployment and maintenance. But it was still in the "weak facility navigation" mode.
2D LiDAR, i.e. single-beam LiDAR, can scan only one surface. There’s no height information in the imaging results and it’s difficult to identify hanging obstacles. Moreover, it is not sensitive to the shelf placement position changes, resulting in insufficient flexibility of forklifts. This technology can only be applied to indoor scenarios with relatively simple and fixed layout, but struggles to meet the storage flexibility needs.
The increasingly urgent demand for intelligence in the industry and logistics and storage challenged the AGV industry to achieve higher flexibility, universality, safety and reliability. In response, global leading forklift enterprises including HikRobot, Agilox, Seegrid, etc. started to invested in the better-performing 3D LiDAR navigation and obstacle avoidance technology, bringing a new round of navigation technology upgrade to the industry.
3D LiDAR – “eye of intelligent navigation”
3D LiDAR is equivalent to the integration of multiple 2D LiDARs. It can transmit and receive multiple lasers simultaneously to realize 3D imaging, and is widely used in the field of autonomous driving. As the industry grows and demands escalate, 16-beam, 32-beam and other LiDAR products have been gradually applied to the field of AGV.
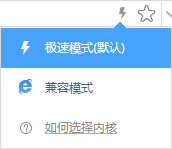
Note: 2D (single-beam) LiDAR imaging (left); 3D (multi-beam) LiDAR imaging (right)
From the above comparison of the point cloud images of 3D LiDAR and 2D LiDAR, we can see that 3D LiDAR can scan 3D space and generate dense 3D point clouds with clear 3D contour of objects and walls and accurate reflectance discrimination, providing abundant accurate and reliable data support for positioning, navigation and obstacle avoidance of AGV.
On the other hand, 3D LiDAR boasts strong detection ability of low reflectivity objects, effective shield against ambient light interference and high power of rain, haze, snow and dust penetration. It can be used in indoor and outdoor complex scenarios, and has significant advantages compared with 2D LiDAR.
Equipped with 3D LiDAR, the AGV’s perception ability will be greatly enhanced to achieve higher peak efficiency, operation accuracy and adaptability to indoor and outdoor complex scenarios in single vehicle operations, to realize flexible and intelligent applications and promote the intelligent transformation of warehouse & storage and logistics.
01
Connect applications in indoor and outdoor scenarios and flexibly adapt to different operation needs
Navigation solutions of AGV currently available on the market are mainly applicable to indoor scenarios. But in reality, in addition to the logistics inside the warehouse, the handling and transportation, loading and unloading operations between the warehouse and outdoor containers are also important links. Both indoor and outdoor scenarios need to be addressed to realize high-efficiency one-stop operation of AGV.

Note: VNE 20 indoor and outdoor balanced unmanned forklift equipped with RS-Bpearl LiDAR
Taking VisionNav Robotics’ VNE 20 indoor and outdoor balanced unmanned forklift as an example, an RS-Bpearl LiDAR is deployed upside down on the top of VNE 20. The LiDAR uses 32 beams to form a 360°×90° hemispherical FoV, which detects obstacles and ground topography changes around the vehicle with no blind spot. For the core application scenarios of VNE20 platform loading and unloading, RS-Bpearl LiDAR can fully detect the topographic changes of the platform ground cuttings and accurately identify the shape, size and edge position of the platform to protect the forklift from falling off the platform.
With the vision-based navigation system developed by VisionNav Robotics, VNE20 has greatly improved the perception and control of the vehicle. In addition, VNE20 is highly interference-resistant, functions well in outdoor scenarios with changing lighting conditions, switches smoothly between indoor and outdoor scenarios, and flexibly adapts to various operation requirements.
02
Integrated navigation and obstacle avoidance to optimize the number of deployed sensors
LiDARs for unmanned forklifts are mainly obstacle avoidance function oriented or navigation function oriented. Previously, AGV manufacturers would choose different products according to different function requirements. But with the development of unmanned forklift navigation and obstacle avoidance algorithm technology and the sharp decline in 3D LiDAR cost in recent years, the AGV industry is attempting to integrate and realize both functions in one LiDAR, which can reduce the number of LiDARs carried by forklifts to reduce cost on the one hand, and help achieve superior navigation and obstacle avoidance performance by using the higher-performance 3D LiDAR and 3D SLAM technology on the other.

Note: SEER and RoboSense
established strategic partnership on the application of
multi-beam LiDAR for unmanned forklifts
For example, the unmanned forklift launched by SEER in 2021 is equipped with RoboSense’s 32-beam LiDAR, RS-Helios. This LiDAR offers horizontal 0°baseline as well as 70°ultra-wide vertical FOV (55°downward), which means that this one LiDAR can realize positioning and navigation and accurate detection of low objects on the forklifts’ driving lanes at the same time, integrating navigation and obstacle avoidance. Navigation and obstacle avoidance through one 3D multi-beam LiDAR not only optimizes the number of sensors on the AGV, but also supports operation in outdoor scenarios better.
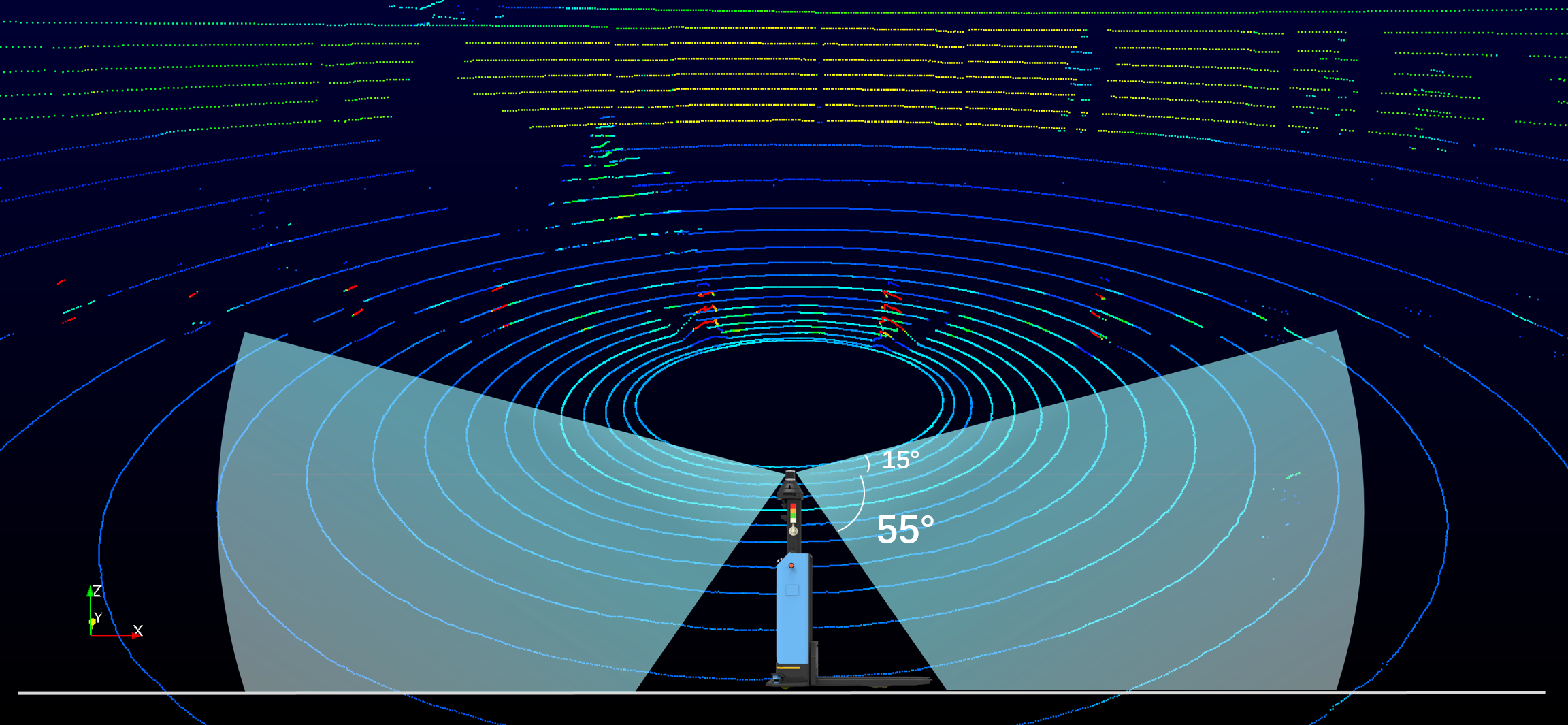
Note: RS-Helios vertical FoV
diagram and outdoor real-time 3D imaging point cloud
deployed on SEER
It is worth noting that based on the ultra-wide vertical FOV of RS-Helios and high density of laser beams scanned, SEER further developed the function of detecting the shape and size of goods and shelves to realize intelligent loading and unloading of goods.
03
Reduce cost and raise efficiency to promote the intelligence empowerment process of AGV
With the development of the autonomous driving industry in the past decade, China’s domestic on-board 3D LiDAR price has been falling from several hundred thousand RMB to below a hundred thousand RMB. Seeing its significant cost performance advantage, more and more manufacturers are considering switching to domestic 3D LiDAR from previous overseas 2D LiDAR.
Domestic LiDAR enterprises represented by RoboSense are entering the AGV market. As the leader in smart LiDAR, RoboSense has been recognized by and established nominated cooperation with multiple car enterprises including BYD, Lotus Cars, WM Motor and ZEEKR for more than 40 models in the field of intelligent driving. At present, RoboSense’s two medium and low speed autonomous driving LiDAR products, RS-Bpearl and RS-Helios, have obtained orders from domestic and overseas leading enterprises including SEER, Mooe Robot, Agilox and Seegrid, and become the rising stars of the global AGV industry.

Note: Agilox equipped with RS-Bpearl LiDAR
How can domestic unmanned forklift enterprises, with the domestic market penetration rate of less than 1%, leverage the strengths of domestic perception-based navigation technology industrial chain, cut costs and boost efficiency in the post-COVID era, fulfill transformative intelligent upgrade and “overtake” their peers on the global market? This is a topic to be addressed.